
What Is EpiCeram®?
EpiCeram® emulsion is a barrier-repair formulation, which is available by prescription only. It offers a unique, cortisone-free, topical therapy for patients with eczema and atopic dermatitis. EpiCeram® was developed based upon research from the Elias laboratory. Our research group has been concerned for many years with uncovering the means whereby skin prevents water from escaping out of the body – its permeability barrier.
The Science Behind EpiCeram®
Many years ago our laboratory discovered the key principle underlying the skin’s barrier: lipids (or fats) forming of multiple layers of membranes, envelope each cell in the outermost layers of skin cells (the ‘stratum corneum’). Multiple layers of fatty membranes surround multiple layers of ‘dead’ skin cells to form our skin’s surface and generate a highly redundant, hydrophobic structure. This lipid fortress greatly retards the movement of water into or out of the body.
For more about how the skin barrier is formed, sign up to receive our free booklet, “Primer On The Skin Barrier”.
We and others soon discovered that one unusual class of lipids, ceramides, that heretofore had been thought to only be abundant in brain tissue, were also the most abundant lipid in the stratum corneum. As a result, many skin care products have since been developed that contain natural ceramides or, more commonly, synthetic versions of ceramides.
Ceramides – which are large, complex organic compounds – account for about half of all the lipids by molecular weight, and fully 5% of the total weight of the stratum corneum.
Yet, soon thereafter we discovered that the other two lipids (cholesterol and free fatty acids) are also required for the barrier. Indeed, only when we provided all three of the lipids together would the skin heal itself normally after an acute insult, such as after removing layers of outer skin cells with adhesive tapes or washing the skin with harsh soaps (or detergents). Application of a preparation that only contained ceramides actually caused further harm, and the skin was slower to heal. The same was true, if we only applied cholesterol, or only applied fatty acids. The injured barrier was slower than normal to heal when any one class of lipids was given without the other two.
Normally the 3 key lipids in the stratum corneum membranes – cholesterol, ceramides, and free fatty acids – are present with equal numbers of molecules of each class, forming a 1:1:1 molar ratio.
Providing the injured skin with a mixture of the 3 lipids in a 1:1:1 molar ratio allowed normal healing to proceed. Shortly thereafter, we discovered that we could help the skin to heal even faster, if we increased the proportions of any one of the three lipid ingredients to a 3:1:1 ratio. Either ceramides, cholesterol or fatty acids could be the lipid class that was increased 3 fold in the mixture to accelerate healing. We called this 3:1:1 ratio the ‘optimal molar ratio’ for skin barrier repair.
EpiCeram® has an optimal molar ratio of skin barrier lipids wherein ceramides are the predominant lipid class.
EpiCeram® Corrects The Skin Barrier In Atopic Dermatitis
It was the discovery of the optimal mole ratio that served as the basis for the development of EpiCeram® emulsion as a treatment for atopic dermatitis. We and other investigators had discovered that, although the skin in atopic dermatitis is deficient in all three classes of lipids, ceramides are decreased disproportionately. Thus, EpiCeram® was formulated with ceramides as the predominant species, to form an optimal molar ratio of 3 (ceramides): 1 (cholesterol): 1 (fatty acids) in the lipid emulsion.
Another key feature of EpiCeram® is that it restores the skin’s normal acidity, its ‘acid mantle’.
Skin is normally quite acidic. Whereas the interior of the body closely guards in neutral pH (~pH. 7.4), the skin surface is normally maintained in the acidic range (pH~5.0). This so-called ‘acid mantle’ is lost in atopic dermatitis, where the skin pH becomes elevated towards a more neutral pH. To restore the acid mantle, EpiCeram® – and in marked contrast to most other skin care products – is highly acidic.
Restoring the skin’s acid pH can provide an important, additional boost to the strength of the permeability barrier. It also improves skin’s antimicrobial defenses, because ‘bad bugs’ like Staph. aureus do not grow well at an acidic pH. This is particularly important in atopic dermatitis, because overgrowth with Staph. aureus on both skin lesions and often on uninvolved skin is a nearly universal feature of this disorder and closely linked to disease pathogenesis. We added several other beneficial ingredients in the final EpiCeram® formulation. For example, EpiCeram® also contains petrolatum, lanolin and glycerol, that both protect the skin and add substantial moisturizing power.
Evidence That EpiCeram® Works
Many products on the market claim to repair the barrier, but few offer proof of efficacy. In contract, several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of EpiCeram® in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (see 1, 2, 3). Indeed, it has been shown to be effective in atopic dermatitis in even the most severe forms of atopic dermatitis. Certain ingredients in EpiCeram® have been shown to prevent disease relapse (“rebound flares’) and the emergence of side effects, when used along with immune-suppressant forms of treatment, such as topical corticosteroids.
While there are many other types of drug therapy on the market now or still under development for the treatment of the inflammation in atopic dermatitis, none of these other agents address the underlying barrier abnormality in atopic dermatitis. Immunosuppressants, like corticosteroids or calcineurin-inhibitors, as well as the new ‘biologics’, all carry the potential for serious side effects, and many of these newer agents are prohibitively expensive. Also, none of these agents prevent disease relapse, potentially requiring patients to continue their use for many months-to-years.
Moreover, studies that are underway all over the world to determine the efficacy of EpiCeram® – not only in the treatment, but also in the prevention of the development of other allergic disorders, such as asthma and hay fever. One recent study has found that EpiCeram® was able to retard the development of food allergies during in infancy. Stayed tuned.
Isn’t EpiCeram® just an expensive moisturizer?
EpiCeram® is definitely not just another moisturizer. To understand this, it is important to understand the difference between how skin handles products that contain ‘physiologic’ lipids – lipids that are found in the body – vs. those that are foreign to it. Cholesterol, free fatty acids and ceramides are all manufactured in the skin; they are physiologic lipids. Petrolatum is a byproduct of fossil fuels; its long chain hydrocarbons are not natural or physiologic to skin. These two types of lipid have very different destinies when applied to the skin surface.
Non-physiologic lipids form a film on the skin surface. They can trap moisture underneath, and can act therefore as effective moisturizers. Until, that is, they wear or rub off – usually in a few hours. In contrast, those physiologic lipids that are natural to skin percolate down through the stratum corneum until they reach the living epidermal cells. These cells take them up, package them into their “delivery wagons” – a small organelle, called the epidermal lamellar body – and expel them back out into the stratum corneum, where they organize to form its water-proofing lipid membranes.
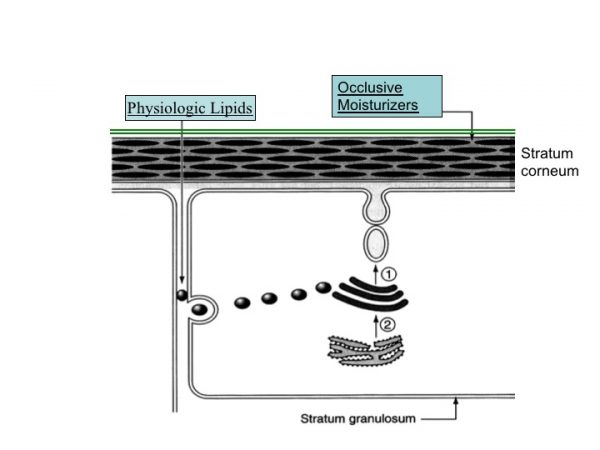
When these physiologic lipids are applied in the right ratios (1:1:1 or 3:1:1), they are able to form normal lamellar membrane structures and, thereby, repair the barrier. If present in the wrong ratio (for example, in a formulation that only contains ceramides), they will not form normal membranes and the barrier may actually become leakier.
Disclaimer
EpiCeram® was developed from research conduced by the Elias laboratory. Dr. Peter Elias is a co-inventor of the product, which is licensed by the University of California, and marketed by Primus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
I apply other nonsteroidal creams 4 times daily (every 4 hours). When should I apply EpiCeram?
1. Before my topical med or after? How long before or after?
I worry the topical will ruin Epiceram time release OR EpiCeram will block or interfere with the topicals.
We would suggest that you apply EpiCeram first, and if you can wait 15-30 minutes before you apply your other topical medication.
Hi,
I have a huge problem with a weak skin barrier after years with harsh skin care products as well as oral treatments (three rounds of isotretinoin due to perioral dermatitis/rosacea). My facial skin is always uncomfortable and stings/burns through out the day as the skin produces sebum which irritates my skin. Could the Epiceram be an alternative for me?
Thank you very much for responding!
There have been no formal studies looking at Epiceram in rosacea or perioral dermatitis. However, we think it could be useful in many settings when the skin is irritated and inflamed and it may be worth a try in your situation. It will require your doctor’s prescription, however.